
Only the femur (your thigh bone) is longer. Your tibia is the second longest bone in your body. If you ever break your tibia - called a tibial fracture - your provider might use some of these terms to describe where your bone was damaged. It includes the:Īll of these parts and labels are usually more for your healthcare provider to use as they describe where you’re having pain or issues. It meets your fibula and calcaneus (ankle bone). The lower (distal) end of your tibia forms the top of your ankle joint. The shaft is the long portion of the tibia that supports your weight and forms the structure of your shin. The upper (proximal) end of your tibia forms the bottom of your knee joint. The tibia has a flat, shelf-like end where it forms part of your knee, a long middle shaft and a notch at the bottom where it forms your ankle.Įven though it’s one long bone, your tibia is made up of several parts. The fibula doesn’t support as much weight and mostly provides structural support to your leg. The tibia is weight-bearing, which means it supports your body when you stand and move. The fibula is closer to the outside of your body (lateral) than the tibia. The tibia is longer and forms part of your knee at its top (proximal) end and your ankle at its lower (distal) end. The tibia and fibula are the two bones that form your lower leg. It’s closer to the inside of your body (medial) than the fibula. The tibia runs from just under your knee to your ankle. To the patellar tendon area.The tibia is the bigger of the two bones in your lower leg. The gastrocnemius heads, (to prevent rotation) and applies load At this stage X raysĬan be taken out of plaster, as callus formation is better assessedįor mid shaft or lower fractures a patellar bearing cast often speeds With only replacements when seen at the clinic. Once the fracture starts stabilising after the Once the doctor is satisfied with alignment, the patient is followed If satisfactoryĪlignment is obtained, repair the plaster with more pop bandages Once the plaster gap has been opened retain The cut willīe made so that an opening wedge can be made on the lateral sideĭeepening the cut. X rays show acceptable length, but valgus angulation Once the desired result is achieved repair Opening the gap in he plaster and holding it with a wooden block.Ĭheck X rays are taken. The plaster is sawed open at the fracture level - keep a intact ExtendĪ line at right angles to the shaft at both sides of the fracture Measure the angulation on the x ray (leg still in plaster). Method will fail and a remanipulation or possibly open reduction and If there is unacceptable loss of length this If there is angulation wedgingĬan be done of the cast. The next follow up can be at one or two weeks. Or instruct him to return for a circulation check the following day.

Take a check X Ray to confirm your reduction. An assistant can pullĭownwards on the ankle to maintain the reduction The below knee portion can be completed first.
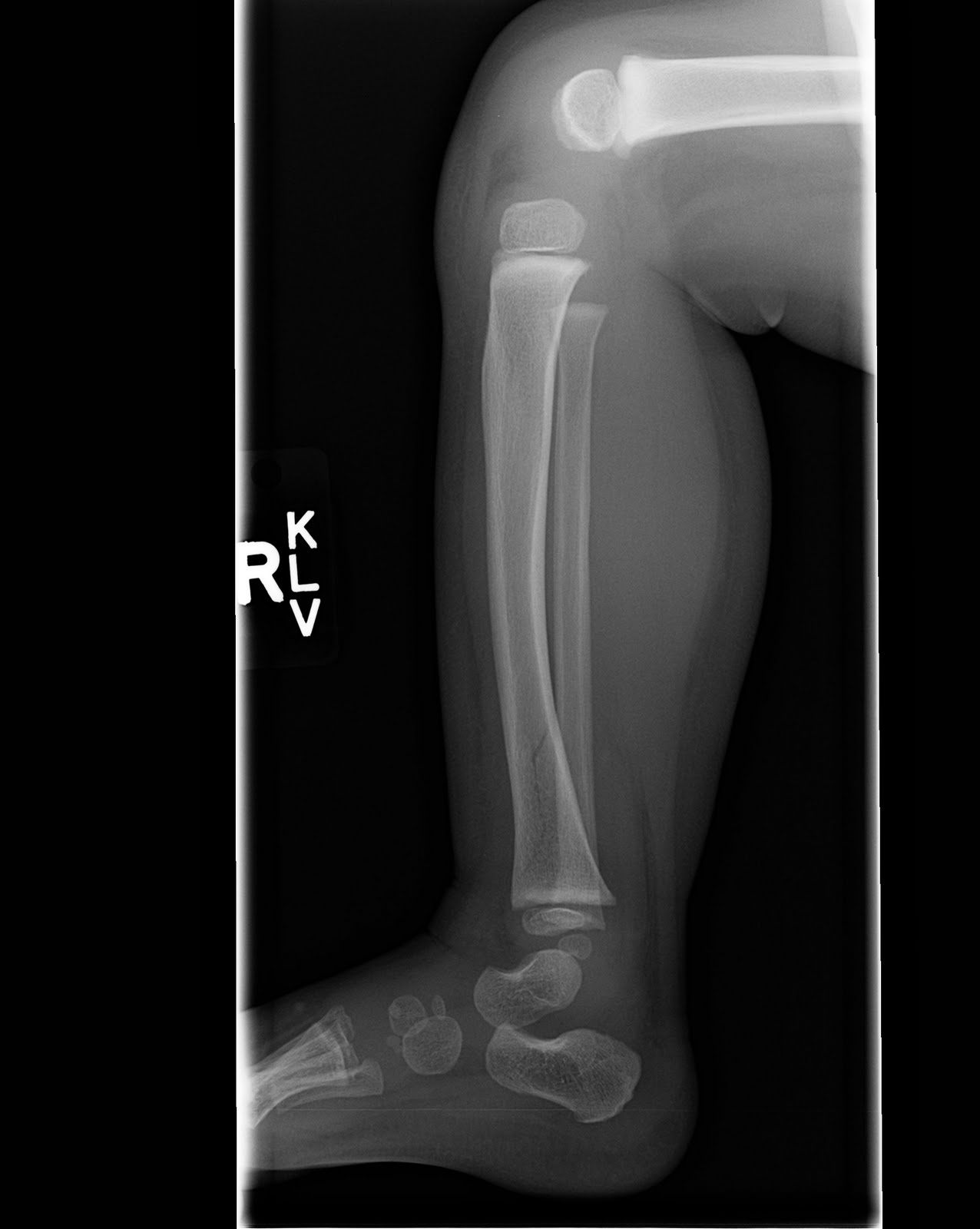

Use a generalĪnesthetic if there is overlapping of bones, or difficulty is expected. If the fracture is minimallyĭisplaced a general anesthetic may not be necessary. Stable and minimally displaced fractures can be treated conservativelyīy reduction and an above knee cast. Here the decision can be made as to whether the wound communicated with the fracture or not.

Wounds near the fracture need exploration in theater. Make sure there is no nerve fallout, especially the peroneal nerve (drop foot).Īny wounds present alert you to te presence of an open fracture. To look for other injuries, including chest and abdominal trauma.Ĭheck for other fractures and dislocations, especially of the ipsilateralĬheck for diatal pulses. Tibial fractures are often due to high velocity trauma. Due to the subcutaneous nature of the distal part of the anterior


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
